Language is the bedrock of human interaction, a conduit that bridges cultures, thoughts, and emotions. The intricacies of mastering a new language have fascinated scholars, educators, and neuroscientists alike for centuries. In recent decades, advancements in neuroscience have shed light on the intricate workings of the brain in its quest to absorb, process, and utilize new languages.
The Neurological Ballet of Language Acquisition
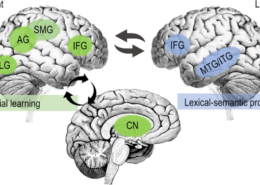
Neuroscience has unveiled a complex dance within the brain when learning a new language. It reveals a symphony of activity involving various regions, each playing a crucial role in the linguistic puzzle. The left hemisphere, particularly the frontal and temporal lobes, is often hailed as the language processing hub. Here, Broca’s area and Wernicke’s area work tirelessly, handling the production and comprehension of language, respectively.
Recent studies employing neuroimaging techniques like fMRI and EEG have unraveled deeper insights. They showcase the dynamic shifts in brain activity during language learning, highlighting the plasticity of the brain, the ability to rewire and adapt.
The Impact of Age on Language Acquisition
The brain’s receptiveness to new languages varies across ages. Childhood presents a unique window of opportunity, where the brain is highly malleable, effortlessly absorbing linguistic nuances. However, this doesn’t discount adults’ ability to learn languages; instead, it illuminates the differences in learning mechanisms. Adults may face challenges but possess cognitive advantages, such as analytical skills and metalinguistic awareness.
Strategies to Optimize Language Learning through Neuroscience
Understanding the brain’s role in acquiring languages allows for the development of effective learning strategies. Techniques like spaced repetition, immersive experiences, and multimodal learning capitalize on the brain’s neuroplasticity. Utilizing multiple senses—listening, speaking, reading, and writing—engages diverse brain regions, reinforcing neural connections crucial for language acquisition.
Moreover, emotional engagement fuels language learning. Creating meaningful connections, whether through storytelling or personal associations, activates the brain’s limbic system, enhancing retention and retrieval.
Overcoming Challenges and Harnessing Technology
Challenges abound in language learning, including grammar complexities, vocabulary retention, and fear of making mistakes. However, neuroscience paves the way for innovative solutions. Technology, with its array of language-learning apps, virtual reality experiences, and AI-driven tutors, leverages neuroscientific principles to personalize learning, adapt to individual needs, and provide instant feedback, enhancing the learning curve.
A Call to Embrace the Neuroscientific Insights
Neuroscience holds the key to revolutionizing language education. By understanding the brain’s intricate mechanisms, educators and learners can tailor approaches that align with the brain’s natural inclinations. This isn’t merely about acquiring words and grammar but fostering a deeper connection with the culture, emotions, and essence of a language.
In this era of interconnectedness, linguistic proficiency opens doors to opportunities, fosters empathy, and transcends barriers. Embracing the insights from neuroscience in language learning isn’t just an option, it’s a gateway to unlocking the full potential of the human brain in its pursuit of linguistic mastery.
The amalgamation of neuroscience and language learning isn’t just a scientific endeavor; it’s a celebration of our brain’s incredible capacity to adapt, evolve, and transcend boundaries one linguistic neuron at a time.