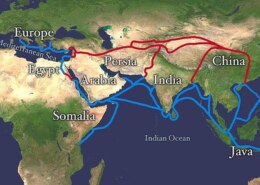
The Silk Road wasn’t a single road but a vast network of trade routes weaving across Asia, linking China, Central Asia, the Middle East, and Europe. Named for the prized Chinese silk that traveled westward, the route also carried spices, precious metals, textiles, art, and much more.
Travelers along the Silk Road included merchants, missionaries, soldiers, and explorers. It was a melting pot of cultures, languages, and religions.
1. Connecting Economies Through Trade
The Silk Road enabled goods to flow between regions that had rarely interacted before. Chinese silk, Indian spices, Persian carpets, and Roman glassware found new markets, sparking economic growth and prosperity in many empires.
This exchange wasn’t just about goods—it was about ideas on how to make and trade them better. Innovations like papermaking and gunpowder spread along the route, eventually reaching Europe and transforming societies there.
2. Cultural Exchange and Religious Spread
Beyond trade, the Silk Road was a conduit for cultural and religious ideas. Buddhism spread from India into Central Asia and China, while Islam, Christianity, and Zoroastrianism also traveled with merchants and missionaries.
Art, music, and literature from different regions influenced each other, creating a rich tapestry of cultural exchange that enriched societies along the route.
3. Technological and Scientific Innovations
The Silk Road was a highway for knowledge. Techniques like silk weaving, paper production, and even medicinal knowledge traveled between East and West.
Chinese inventions such as the compass and gunpowder reached the West through Silk Road contacts, playing a crucial role in world history.
4. The Role of Cities and Oases
Key cities and oases—like Samarkand, Kashgar, and Dunhuang—served as vibrant hubs for commerce and culture. They offered rest and resupply points for travelers, while also becoming centers of learning and art.
These cities blended diverse cultures, creating unique communities where merchants, scholars, and artisans interacted daily.
5. The Silk Road’s Legacy Today
Though the Silk Road declined after the rise of maritime trade routes, its legacy lives on. The idea of connecting distant cultures for mutual benefit remains relevant, inspiring modern initiatives like China’s Belt and Road Initiative.
The Silk Road reminds us that cooperation and exchange across cultures can drive progress, innovation, and peace.