Introduction
A Cyclopropane Manufacturing Plant Project Report outlines the setup, processes, and operational considerations for establishing a plant dedicated to producing cyclopropane. Cyclopropane is a highly reactive organic compound with the molecular formula C3H6, known for its unique properties and applications in various industries. This hydrocarbon is primarily used as an anaesthetic in medical fields, in the production of other chemicals, and in some specific industrial processes. With the growing demand for specialized chemicals and applications in sectors like pharmaceuticals, the demand for cyclopropane is poised for steady growth. This report provides an in-depth analysis of the market dynamics, production processes, equipment, raw materials, and financial aspects of establishing a cyclopropane manufacturing plant.
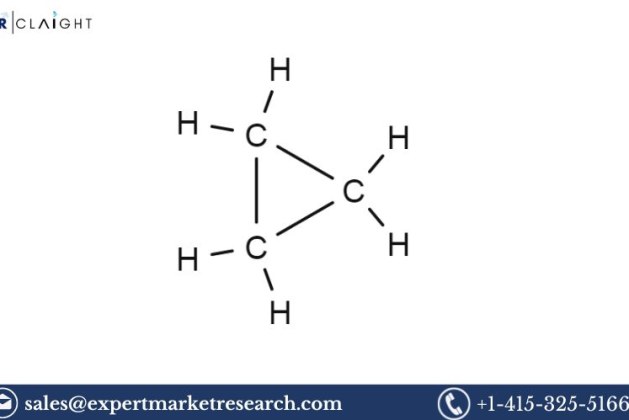
What is Cyclopropane?
Cyclopropane is a cyclic compound consisting of three carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms, forming a three-membered ring structure. It is a colourless, flammable gas at room temperature and is known for its unique chemical reactivity due to the strain in its three-membered ring. Cyclopropane was historically used as an anaesthetic agent in surgeries, though it has largely been replaced by newer agents due to safety concerns. Despite this, it is still utilized in chemical synthesis, particularly for creating chemicals like propene and other intermediates in the petrochemical industry.
Cyclopropane has industrial applications as a propellant, solvent, and in the synthesis of other valuable chemicals. Its highly strained molecular structure makes it useful in organic synthesis, particularly in the creation of valuable chemicals like epoxy compounds, which are used in the production of resins and coatings.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
Key Considerations for Setting Up a Cyclopropane Manufacturing Plant
1. Raw Materials
The primary raw material for cyclopropane production is ethylene (C2H4), which is typically derived from petroleum or natural gas. Ethylene is mixed with another reactant, usually a halogenated compound like chlorine or bromine, in the presence of a catalyst to initiate the reaction that forms cyclopropane.
Key raw materials include:
Ethylene: The primary feedstock for cyclopropane production.
Halogenated Compounds: Chlorine, bromine, or iodine may be used as a reactant to help form cyclopropane.
Catalysts: Specific catalysts are required to accelerate the reaction process, such as aluminium chloride (AlCl3) or other Lewis acids.
Solvents: Solvents like ether or hydrocarbons may be used in the production process to facilitate the reactions.
2. Machinery and Equipment
The production of cyclopropane requires specialized equipment to handle the chemical reactions involved. Key machinery includes:
Reactor Vessel: A pressure vessel where the chemical reaction between ethylene and halogenated compounds occurs. The reactor must be designed to withstand high pressure and temperature conditions.
Distillation Columns: Cyclopropane is separated from the reaction mixture through distillation. Distillation columns help in purifying cyclopropane and separating it from other by-products.
Cooling Systems: As cyclopropane is highly volatile, cooling systems are essential to condense the cyclopropane gas into a liquid state for storage and transportation.
Compressor: Compressors are needed to compress cyclopropane into a liquid form for storage and transport, as it is a gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure.
Storage Tanks: Specially designed pressure-resistant tanks for storing cyclopropane once it has been condensed into a liquid form.
Safety Equipment: Given cyclopropane’s flammability and volatility, advanced safety systems, including gas detectors, fire suppression systems, and ventilation systems, are necessary to ensure a safe working environment.
3. Manufacturing Process
The cyclopropane production process typically follows a reaction known as the cyclopropanation reaction. The process involves the following steps:
Feed Preparation: Ethylene is mixed with a halogenated compound, usually chlorine or bromine, in the presence of a catalyst (e.g., aluminium chloride or other Lewis acids) to initiate the reaction.
Cyclopropanation Reaction: In the reactor vessel, the feed mixture undergoes a highly exothermic reaction, resulting in the formation of cyclopropane and by-products such as hydrochloric or hydrobromic acid (depending on the halogen used).
Separation: After the reaction, the mixture contains cyclopropane, along with other by-products like unreacted ethylene, solvents, and the halogenated compounds. These are separated using distillation columns.
Purification: The cyclopropane is further purified to remove impurities such as residual solvents or unreacted raw materials. This is done using fractional distillation and filtration.
Compression and Storage: The purified cyclopropane is then compressed into a liquid form and stored in pressure tanks. Cyclopropane is typically stored as a liquid at low temperatures or high pressures to maintain its state.
4. Plant Layout and Design
The design of a cyclopropane manufacturing plant is crucial for efficient production and maintaining safety standards. The layout should include:
Raw Material Storage: Dedicated storage tanks for ethylene, halogenated compounds, and solvents. These storage areas must be secure and properly ventilated.
Reaction Area: The reactor vessels and associated piping systems, where the cyclopropanation reaction occurs. This area needs to be designed for high-temperature and high-pressure conditions.
Purification and Separation Area: Distillation columns, filtration systems, and cooling units where cyclopropane is separated and purified.
Storage and Distribution: The final product is stored in specialized pressure tanks. Adequate space is required for safe storage and easy access for transportation.
Safety and Control Systems: The plant must have advanced safety features, including emergency shutdown systems, gas leak detectors, fire suppression systems, and secure handling of hazardous chemicals.
5. Workforce and Skills
A skilled workforce is essential for the successful operation of a cyclopropane manufacturing plant. Key roles include:
Chemical Engineers: Responsible for overseeing the production process, ensuring efficiency, and optimizing the reaction conditions.
Production Operators: Workers who operate the reactors, distillation units, and storage systems.
Quality Control Inspectors: Personnel responsible for ensuring that the cyclopropane meets the required purity and safety standards.
Safety Officers: Professionals who monitor safety protocols, ensure regulatory compliance, and conduct regular safety audits.
Maintenance Technicians: Skilled workers who maintain and troubleshoot the equipment and machinery.
6. Environmental and Safety Considerations
Given that cyclopropane is a flammable and hazardous substance, the plant must adhere to strict safety and environmental regulations. Some important considerations include:
Emission Control: Cyclopropane production involves potentially harmful by-products like chlorine gas or hydrochloric acid. The plant should incorporate emission control systems to neutralize or capture these substances.
Waste Management: By-products like acids or solvents must be disposed of properly, either through recycling or treatment to neutralize their effects.
Explosion Prevention: The plant must have explosion-proof equipment and regular monitoring of gas concentrations to prevent accidents.
Market Demand and Applications
Applications of Cyclopropane
Pharmaceuticals: Historically used as an anaesthetic, cyclopropane is still studied for its potential in medical applications.
Chemical Synthesis: Cyclopropane is a valuable intermediate in the production of various chemicals, such as propene and other epoxides, which are used in the manufacture of plastics, resins, and other chemical products.
Propellant and Solvent: In some niche markets, cyclopropane is used as a propellant or solvent in the formulation of certain products.
Market Growth
The demand for cyclopropane is primarily driven by its applications in organic chemistry and pharmaceuticals. The rise of the petrochemical industry, advancements in drug manufacturing, and increased use in specialty chemical production are key growth drivers.
Cost Breakdown and Investment
The investment required for setting up a cyclopropane manufacturing plant involves several key areas:
Land Acquisition: Costs for acquiring land or renting space for the plant.
Machinery and Equipment: Investment in reactors, distillation units, compressors, and storage tanks.
Raw Materials: Ethylene, halogenated compounds, and catalysts.
Labor: Skilled workforce and operational staff.
Regulatory Compliance: Meeting environmental and safety standards.
Utilities: Energy costs, water, and waste management.
FAQs
1. What is cyclopropane used for?
Cyclopropane is used in pharmaceuticals as an anaesthetic, in chemical synthesis to create other compounds, and as a propellant and solvent in certain industries.
2. Is cyclopropane flammable?
Yes, cyclopropane is highly flammable and requires careful handling, particularly in storage and transportation.
3. Can cyclopropane be stored at room temperature?
Cyclopropane is typically stored as a liquid at low temperatures or high pressures to prevent it from evaporating.
4. What raw materials are required for cyclopropane production?
The main raw materials for cyclopropane production are ethylene, halogenated compounds like chlorine or bromine, and catalysts.
5. Is cyclopropane still used in anaesthesia?
While cyclopropane was widely used as an anaesthetic in the past, it has been largely replaced by other agents due to safety concerns. However, it is still studied for potential medical applications.
Media Contact:
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: http://www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au



Leave a comment